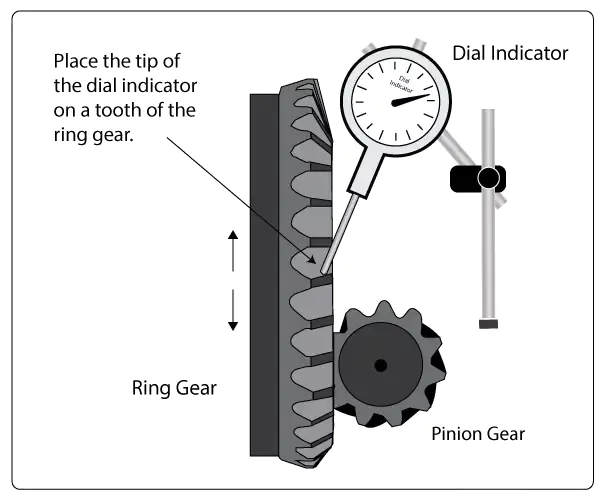
In 2025, automotive engineering is moving faster than ever. Electrification, lightweight design, and sustainability are no longer fringe concepts — they’re industry standards. Right at the center of this transformation are ring and pinion gears, essential to torque delivery and differential function.
These gear pairs manage the transition of power from engine (or motor) to wheels, balancing torque between left and right axles and ensuring smooth, responsive handling. As expectations shift, so too must the materials, geometry, and manufacturing processes behind these components.
Southeast Asia is a growing force in this shift — both as a production hub and as a rising consumer market. But so is the rest of the world, from North America’s off-road sector to Europe’s performance EV segment. Here’s how the industry is adapting.
Advanced Materials Driving Performance
Why Traditional Steel Is No Longer Enough
Ring and pinion gears have historically relied on hardened steels — but modern vehicles demand more. High torque loads, extended maintenance intervals, and compact layouts make older materials a liability.
Chrome-Moly and Boron-Enhanced Steels Gain Ground
Manufacturers are turning to alloys infused with chromium and molybdenum for superior strength and fatigue resistance. These materials handle heavier loads, making them ideal for commercial trucks and high-horsepower builds.
Powder Metallurgy Enters the Mainstream
In high-volume production, powder metallurgy offers excellent strength-to-weight ratios and cost efficiency. It allows for fine detail and consistency, ideal for precision pinion shapes in compact gearboxes.
Lightweight Metals for Performance Applications
Titanium blends and aluminum-based gear structures are now being tested in racing and EV applications. Reducing rotating mass can noticeably improve acceleration and efficiency — especially important in Southeast Asia’s electric two-wheel and light commercial vehicle sectors.
Precision Manufacturing Techniques
CNC and 5-Axis Machining Raise the Standard
Modern gear manufacturing depends on precision. With 5-axis CNC machines, gear teeth can be cut with exacting accuracy, ensuring tight tolerances and minimal backlash — critical for high-RPM electric drivetrains.

CAD and Simulation Tools Improve Efficiency
Computer-aided design now plays a foundational role. Engineers simulate gear behavior under thermal expansion, torque load, and misalignment — well before anything is produced.
3D Printing for Prototyping and Niche Builds
While additive manufacturing isn’t yet viable for mass-market gears, it’s revolutionizing early-stage development and specialty parts. Niche racing teams and R&D centers are using metal 3D printing for fast iteration.
Inline Quality Monitoring with AI
Factories are integrating machine learning and IoT systems to inspect gears during production. These smart systems detect micro-defects and deviations instantly — improving output quality and reducing waste.
The EV Impact on Gear Design
Instant Torque Changes Everything
Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors deliver peak torque from zero RPM. This places new demands on gear hardness, shape, and engagement profiles.
Noise Becomes a Major Concern
Electric drivetrains are quiet — which means differential noise stands out. Manufacturers are reengineering tooth profiles and material pairings to reduce high-pitched whine and harmonic vibration.
Hypoid and Helical Designs Take Over
Flat-cut gears are giving way to helical and hypoid styles, which engage more smoothly and reduce NVH (noise, vibration, harshness). These are now common in EVs across all classes.
Compact Integration with E-Axles
E-axles integrate motors, gearsets, and differentials into a single sealed unit. This trend requires gear designs that can operate under tighter space constraints with improved thermal performance.
NVH Optimization
What Is NVH and Why It Matters
NVH — noise, vibration, and harshness — used to be a secondary concern. In 2025, it’s a deal-breaker. Customers expect smooth, silent operation, especially in EVs and luxury vehicles.
Gear Geometry for Quiet Operation
Subtle geometry modifications like tip relief and profile crowning reduce gear whine and meshing shock. These tweaks are calculated using multi-body dynamics simulations to predict sound frequency and intensity.
Advanced Housing and Mount Damping
Gear noise doesn’t just come from the teeth — it resonates through housings. Modern designs include acoustic damping materials and suspended mounts to absorb vibration before it reaches the cabin.
Composite and Polymer Dampers
Low-frequency gear hum is often managed with integrated polymer inserts or vibration isolators. These solutions are especially popular in compact city EVs across Southeast Asia.
Sustainability in Gear Production
Cleaner Heat Treatment Processes
Heat treating is energy-intensive. Manufacturers are shifting to vacuum carburizing and low-pressure nitriding to reduce emissions and energy use without compromising surface hardness.
Recyclable Alloys and Material Reuse
High-strength alloys that can be fully recycled are gaining favor, especially in Europe and Japan. These materials support circular manufacturing models and long-term resource planning.
Lower-Impact Lubrication Solutions
Longer-lasting synthetic lubricants, bio-based oils, and sealed-for-life systems reduce fluid waste and protect internal gear faces from wear in extended-use EV platforms.
Sustainability Drives Cost Efficiency
In Southeast Asia, sustainability is also an economic tool. Energy-efficient processes and recyclable materials reduce total cost — making advanced ring and pinion gears more accessible to growing fleets.
What’s Next for Ring and Pinion Technology?
Real-Time Monitoring with Embedded Sensors
Emerging systems use onboard sensors to track load, temperature, and vibration. This data enables predictive maintenance — ideal for logistics companies and fleet managers.
Smart Materials That Adapt Under Load
Research into adaptive alloys is accelerating. Future gearsets may automatically harden, flex, or dampen depending on driving conditions.
The Role of Southeast Asia in Global Gear Innovation
With its manufacturing scale, cost advantage, and rising EV sector, Southeast Asia is becoming more than just a supplier — it’s shaping the next generation of drivetrain technology.
Conclusion
Ring and pinion gears may seem like a legacy component, but in 2025, they’re at the cutting edge of automotive innovation. From advanced materials and silent-running geometries to integrated smart features and eco-friendly production, gear systems are being reengineered for the future.
Whether you’re a performance builder in the U.S., a fleet manager in Southeast Asia, or an engineer working on next-gen EVs, understanding these trends gives you an edge. The gears are changing — and staying ahead means evolving with them.