When it comes to vehicle drivetrain performance, few components are as crucial as the ring and pinion gears. These gears form the heart of the differential, controlling how power is distributed from the engine to the wheels. Understanding their function, design, and maintenance is essential for anyone involved in automotive repair, vehicle modification, or performance tuning. This article provides a detailed explanation of ring and pinion gears, their importance, types, installation considerations, and common issues, offering insights that help vehicle owners and professionals alike make informed decisions.

What Are Ring and Pinion Gears?
Ring and pinion gears are a matched set of gears found inside a vehicle’s differential. The pinion gear is attached to the driveshaft and transfers rotational force into the ring gear, which is mounted on the differential carrier. Together, they allow the differential to transmit power to the wheels at a precise gear ratio.
The primary purpose of these gears is to convert the rotational direction from the driveshaft to the axle shafts while providing a reduction in speed and an increase in torque. This process is essential for smooth and efficient vehicle operation, especially in rear-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, and off-road vehicles.
How Ring and Pinion Gears Work
A well-matched set of ring and pinion gears ensures that:
- Power is efficiently transmitted from the driveshaft to the wheels.
- Vehicle handling remains smooth, especially during turns.
- Noise and vibration are minimized.
The efficiency of this system relies heavily on proper gear meshing, backlash adjustment, and pinion depth. Any deviation in these parameters can lead to uneven wear, excessive noise, or even gear failure.
Types of Ring and Pinion Gears
Ring and pinion gears are not one-size-fits-all. They are manufactured in various types to suit different vehicle applications.
1. Standard Spiral Bevel Gears
The most common type, spiral bevel gears, have curved teeth that allow gradual engagement. This design reduces noise and vibration while distributing stress more evenly across the teeth. Standard spiral bevel gears are suitable for most passenger vehicles and light trucks.
2. Hypoid Gears
Hypoid gears are similar to spiral bevel gears but with an offset between the pinion and ring gear axes. This offset allows for smoother engagement and higher torque handling, making hypoid gears ideal for heavy-duty trucks and high-performance vehicles.
3. Custom or Performance Gears
Performance or aftermarket gears often feature modified tooth profiles, higher-grade materials, and specialized heat treatments. These gears are designed for racing, off-road applications, or vehicles requiring unusual gear ratios. Custom gear sets must be matched carefully to ensure proper operation and prevent premature wear.
Gear Ratios and Their Impact
One of the most significant aspects of ring and pinion gears is the gear ratio. The ratio is calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the ring gear by the number of teeth on the pinion gear. For example, a 4.10 gear ratio means that the pinion gear must rotate 4.10 times to turn the ring gear once.
The gear ratio affects several vehicle characteristics:
- Acceleration: Higher numerical ratios (e.g., 4.56:1) increase torque at the wheels, improving acceleration.
- Fuel Efficiency: Lower numerical ratios (e.g., 3.08:1) reduce engine RPM at cruising speed, enhancing fuel economy.
- Towing Capability: Vehicles with heavier loads often benefit from higher ratios to handle increased torque demands.
- Top Speed: Lower ratios allow for higher top speeds without over-revving the engine.
Choosing the correct gear ratio is crucial for balancing performance, efficiency, and drivability. Professional consultation or precise calculation is often recommended for modifications or upgrades.
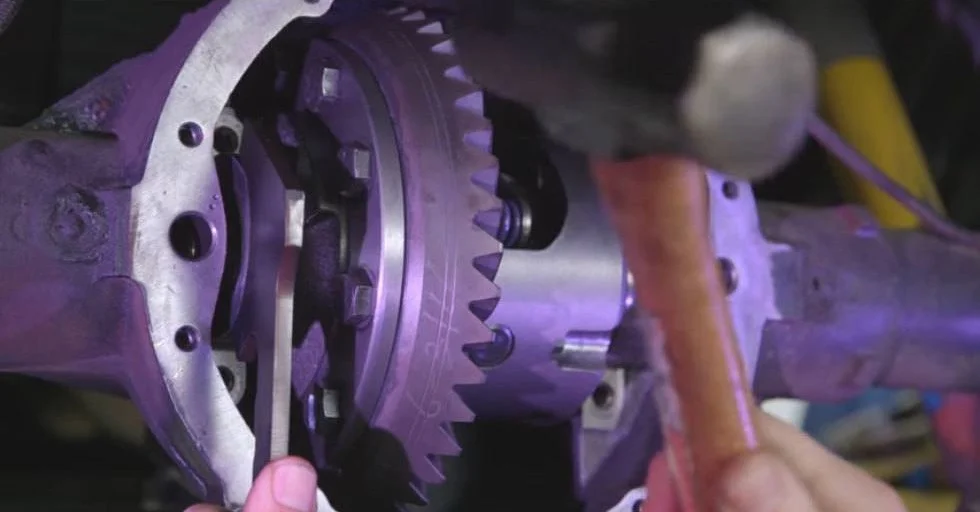
Installation and Adjustment
Installing ring and pinion gears is a precise process that requires specialized tools and knowledge. Key considerations include:
1. Pinion Depth
The distance between the pinion gear and the ring gear must be exact. Incorrect pinion depth can cause uneven wear, noise, and reduced gear life.
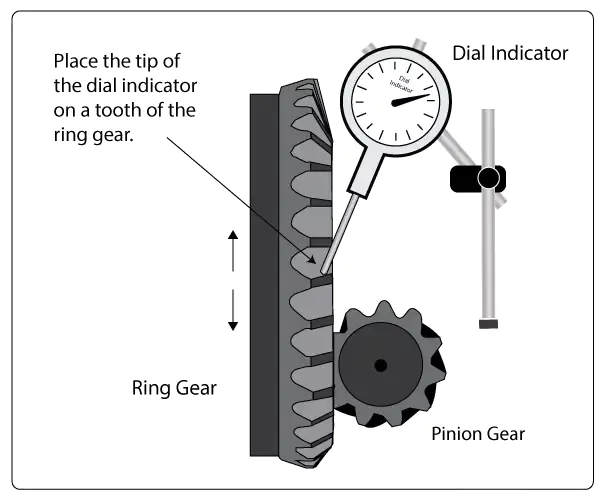
2. Backlash
Backlash is the small gap between the ring gear teeth and pinion teeth. It allows for proper gear engagement without binding. Too much backlash leads to clunking and accelerated wear, while too little can generate heat and noise.
3. Gear Pattern Check
Using marking compound, technicians verify the contact pattern between the pinion and ring gear teeth. The pattern ensures even load distribution and optimal performance.
Even minor deviations in any of these steps can result in premature failure or operational issues. This is why many repair shops emphasize professional installation and calibration.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite their robustness, ring and pinion gears can develop problems over time. Understanding common issues helps with timely maintenance:
1. Noise
Whining, humming, or clunking noises often indicate incorrect backlash, worn teeth, or improper pinion depth.
2. Uneven Wear
Gear teeth can wear unevenly due to misalignment, inadequate lubrication, or excessive load. Regular inspection can detect wear patterns early.
3. Gear Tooth Damage
Chipped or broken teeth usually result from extreme torque, contamination, or poor installation. Damaged teeth require gear replacement to prevent further differential damage.
4. Vibration
Excessive vibration while driving can be linked to pinion misalignment or imbalance in the driveshaft. Diagnosing and correcting these issues ensures smooth operation.
Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance extends the life of ring and pinion gears and ensures consistent performance:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check for noise, wear, and proper lubrication levels.
- Lubrication: Use the manufacturer-recommended gear oil, maintaining correct levels to reduce friction and heat.
- Avoid Overloading: Excessive torque or heavy towing can accelerate gear wear.
- Professional Service: Periodic servicing by qualified technicians ensures correct backlash, pinion depth, and gear pattern.
Adhering to these maintenance practices reduces the likelihood of costly repairs and maintains drivetrain efficiency.
Upgrades and Performance Considerations
For performance enthusiasts, aftermarket ring and pinion gear sets offer several advantages:
- Improved Acceleration: Higher numerical ratios increase torque at the wheels.
- Enhanced Durability: Hardened materials and specialized heat treatments extend gear life.
- Noise Reduction: Optimized tooth profiles reduce gear whine and vibration.
- Custom Ratios: Tailored ratios meet specific performance requirements, such as off-road crawling or drag racing.
While upgrades can enhance vehicle performance, it is essential to ensure compatibility and professional installation to avoid operational issues.
Conclusion
Ring and pinion gears are fundamental to the proper functioning of any vehicle’s drivetrain. Their role in power transfer, torque multiplication, and smooth wheel rotation cannot be overstated. Whether for standard passenger vehicles, heavy-duty trucks, or high-performance modifications, understanding how these gears work, how to maintain them, and how to choose the right gear set is crucial.
Proper installation, careful maintenance, and timely upgrades not only improve vehicle performance but also enhance safety and longevity. By paying attention to gear ratios, tooth patterns, and lubrication, vehicle owners and repair professionals can ensure reliable operation for thousands of miles.
Mastering the intricacies of ring and pinion gears allows automotive professionals, enthusiasts, and engineers to make informed decisions that maximize efficiency, performance, and durability.