When it comes to maintaining and optimizing a vehicle’s differential, understanding the relationship between pinion depth, backlash, and the contact pattern is crucial. These elements directly influence how smoothly the vehicle operates, how efficiently power is transferred to the wheels, and how long the differential components last. Many vehicle owners and mechanics frequently ask: How do adjustments to pinion depth and backlash affect differential performance? This article provides an in-depth look at these concepts and explains how to achieve optimal gear engagement for your differential.
Understanding Pinion Depth
Backlash and Its Importance
Straddle Mount Differentials and Pinion Adjustments

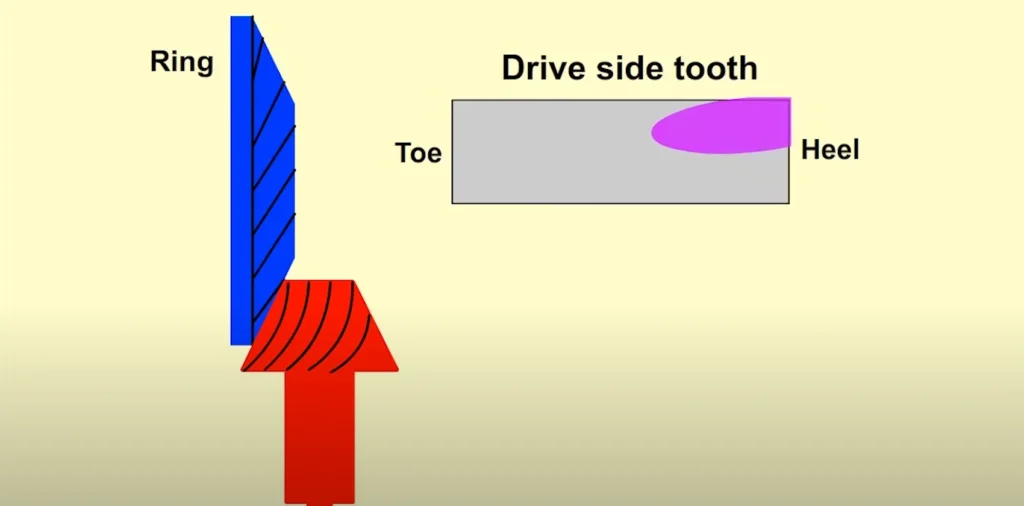
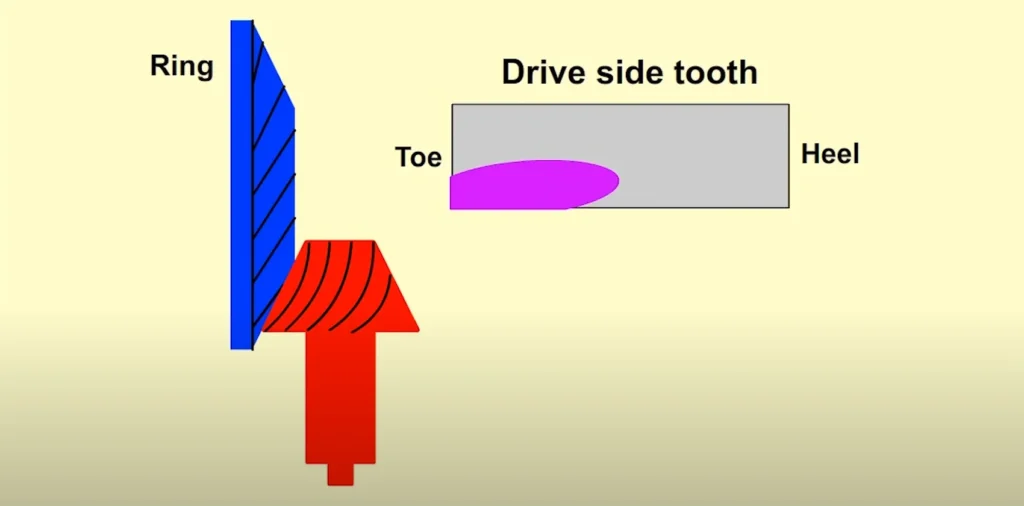
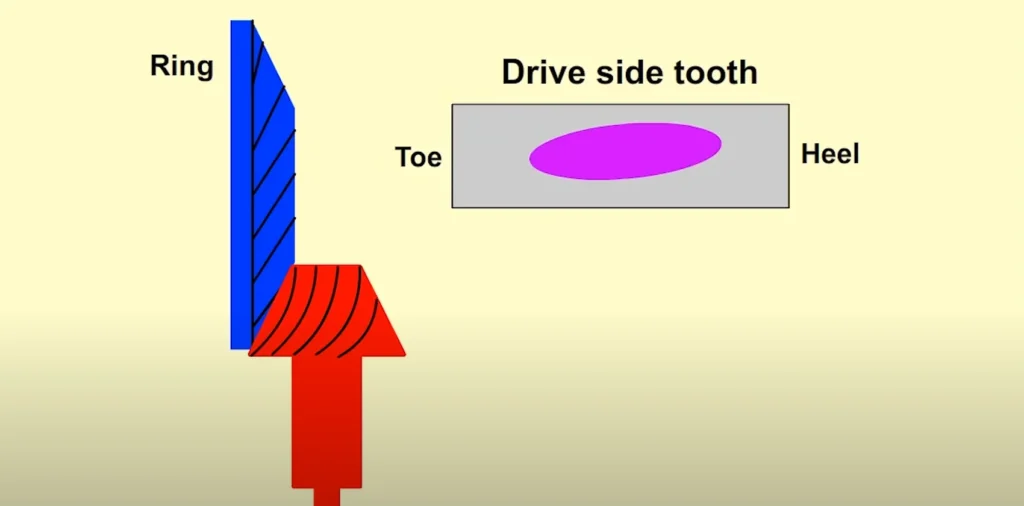
Contact Pattern Analysis
In practice, multiple iterations may be required. Adjustments of as little as 0.010 inches in pinion depth can significantly change the contact pattern. A well-centered pattern ensures that both the drive side and coast side teeth share the load evenly, improving performance and durability.

Step-by-Step Procedure for Pinion Depth Adjustment
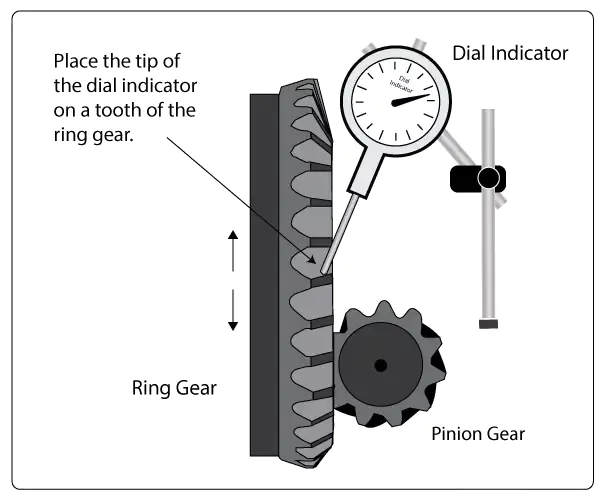
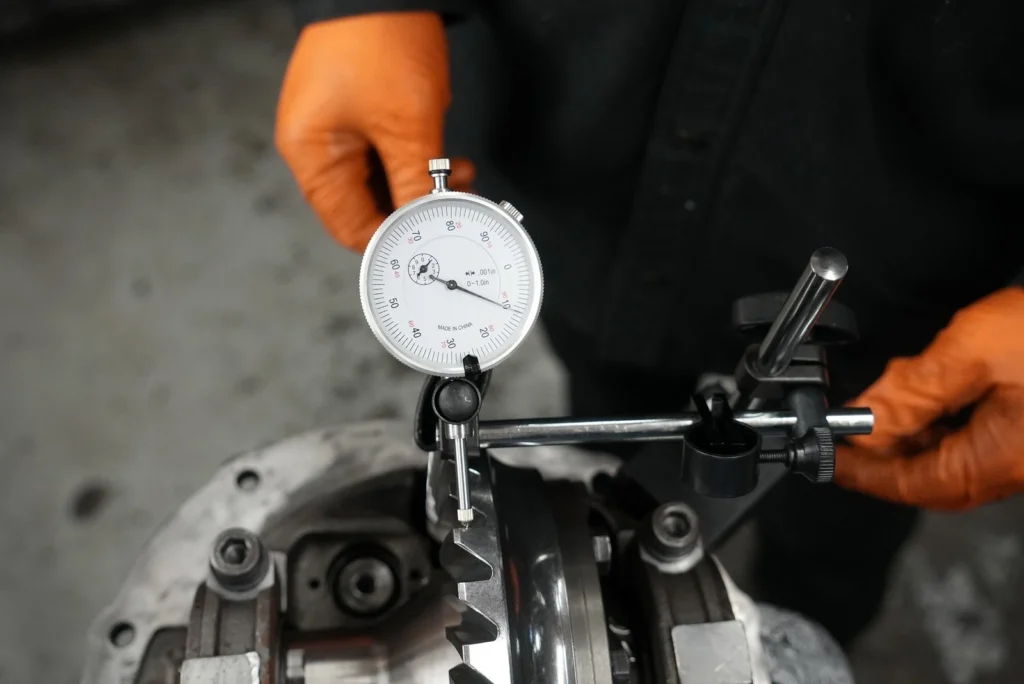
- Measure Initial Pinion Depth: Use a dial indicator to determine the current pinion depth relative to the ring gear centerline. Zero the indicator at this starting position.
- Set Initial Backlash: Adjust the ring gear position to achieve the target backlash, usually around 0.010 inches.
- Apply Gear Marking Compound: Coat two ring gear teeth on both the drive side and coast side.
- Rotate Gears: Run the pinion through the ring gear multiple times to transfer the compound and reveal the contact pattern.
- Analyze Pattern: Check for excessive contact at the toe, heel, or flank.
- Adjust Pinion Depth: Incrementally move the pinion closer or farther from the centerline as needed.
- Readjust Backlash: After each pinion depth adjustment, reset the backlash to specification.
- Repeat Contact Check: Apply fresh gear marking compound and observe the new pattern.
- Finalize Settings: Once the drive side and coast side patterns are well-centered, the pinion depth and backlash adjustments are complete.
Why Proper Adjustment Matters
- Premature Gear Wear: Uneven contact accelerates tooth wear.
- Excessive Noise: Misaligned gears produce whining or clunking sounds.
- Reduced Efficiency: Poor engagement increases friction and reduces power transfer.
- Potential Failure: Severe misalignment can cause gear breakage or differential damage.
Proper adjustment ensures that the differential operates smoothly, quietly, and efficiently. It also extends the lifespan of expensive components, making the investment in careful setup worthwhile.
Tips for DIY Mechanics and Professionals
- Always measure pinion depth and backlash using precise tools like dial indicators.
- Make incremental adjustments and check the contact pattern after each change.
- Keep detailed notes of adjustments to replicate or correct settings if necessary.
- Use high-quality gear marking compound to get a clear contact pattern.
- Ensure the differential is clean and free from debris before making adjustments.
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between pinion depth, backlash, and contact pattern is essential for anyone working on vehicle differentials. Correct adjustments lead to smoother operation, longer gear life, and improved vehicle performance. Whether you are a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, following a systematic approach ensures optimal results.
By carefully measuring pinion depth, setting accurate backlash, and analyzing the contact pattern with gear marking compound, you can achieve the ideal setup for your differential. Remember, even small adjustments can make a significant difference, so patience and precision are key. Properly adjusted differentials not only improve vehicle performance but also contribute to long-term reliability and peace of mind.