When it comes to upgrading your vehicle’s differential, one term that frequently comes up is “carrier break.” For many automotive enthusiasts and professionals, understanding carrier breaks is crucial for selecting the right ring and pinion gears, ensuring proper fitment, and maintaining the longevity of your differential. This article explores the concept of carrier breaks, how they affect gear selection, and what you need to know when upgrading your drivetrain.
What is a Carrier Break?
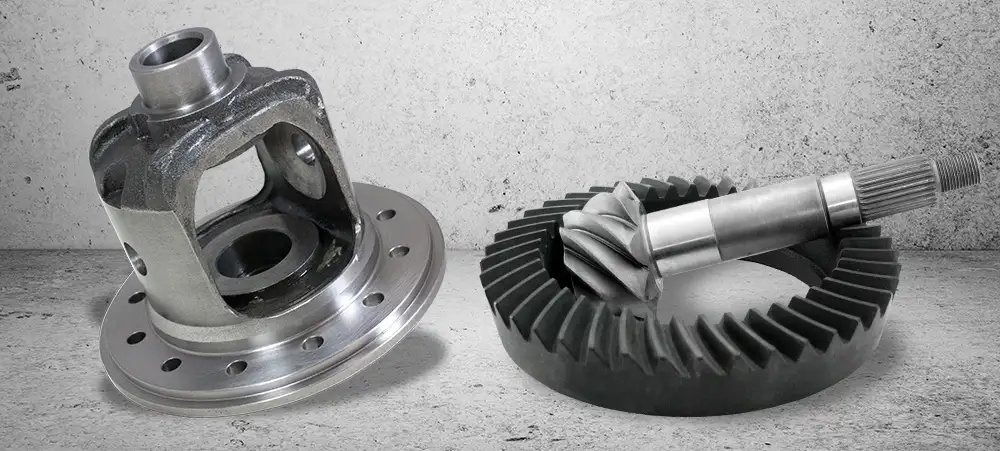
A carrier break occurs when the differential carrier—the housing that holds the ring and pinion gears—cannot accommodate a thicker or larger ring gear required for a specific gear ratio. Simply put, not every differential carrier is compatible with every gear ratio. As gear ratios increase, the physical thickness of the ring gear also increases, and at a certain point, the stock carrier can no longer fit the gear. This point is known as the carrier break.
Understanding carrier breaks is essential because selecting a gear ratio that exceeds your carrier’s limits can lead to installation problems, improper gear mesh, or even catastrophic gear failure.

Why Carrier Breaks Happen
The thickness of the ring gear varies depending on the gear ratio. Lower ratios, such as 3.08:1 or 3.55:1, typically have thinner ring gears that fit most standard carriers. Higher ratios, like 4.56:1 or 5.13:1, require thicker ring gears to handle the increased torque load and maintain structural integrity.
The differential carrier has specific tolerances, and these tolerances define the maximum thickness of the ring gear it can hold. When you try to install a gear that is too thick for the carrier, the ring gear may not align properly, making it impossible to install without modifying the carrier or using a different one.
This limitation is especially important for off-road vehicles, trucks, and performance cars, where gear upgrades are common for torque multiplication and traction optimization.
How to Identify Carrier Breaks
Knowing whether your differential has a carrier break is essential before ordering new gears. Here are some ways to identify it:
- Manufacturer Specifications: Most gear manufacturers provide a chart that lists which carriers can accept specific gear ratios. This is the most reliable method.
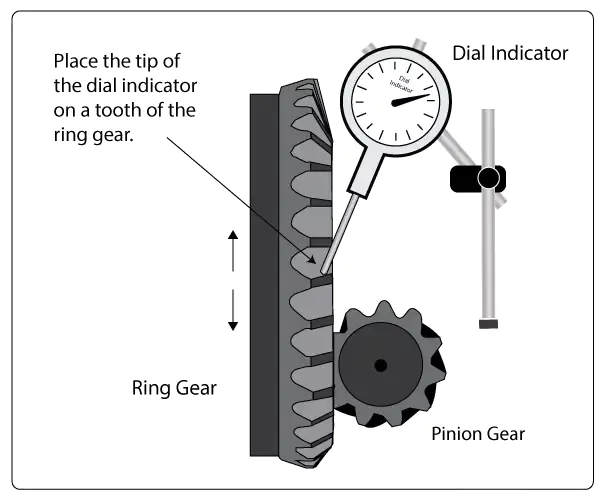
- Physical Measurement: Experienced mechanics may measure the current ring gear and carrier to determine maximum allowable gear thickness.
- Expert Consultation: If unsure, consulting a professional or the manufacturer ensures you avoid incorrect purchases and potential damage.
The Importance of Correct Gear Fitment
- Incorrect Backlash: Backlash is the clearance between the teeth of the ring and pinion gears. If the gears don’t fit the carrier properly, backlash will be off, leading to noise, vibration, or premature wear.
- Gear Misalignment: Misaligned gears can break teeth under load, especially in high-torque or off-road applications.
- Installation Difficulty: Improper fit can make it physically impossible to install the gear without modifying components.
By understanding carrier breaks and ensuring proper fitment, you can prevent these issues and maintain optimal performance.
Upgrading Ring and Pinion Gears
When upgrading to a higher gear ratio, knowing your carrier break point helps you plan properly. Here’s what you should consider:
- Select Compatible Gear Ratios: Choose a ratio that your current carrier can accommodate, or prepare to upgrade the carrier along with the gears.
- Consider Material Strength: High-performance or heavy-duty applications require gears made from durable materials like 8620 steel, CNC-machined for precision, and hardened for strength.
- Check Vehicle Application: Vehicle type, engine output, and intended use (street, track, off-road) all influence which gear ratio and carrier combination is ideal.
Carrier Breaks in Common Vehicles
- Jeep Wrangler Differentials: Often experience a carrier break at around 4.56:1.
- Ford 8.8 Differentials: Stock carriers typically support up to 3.73:1 before requiring an upgrade.
- GM 10-Bolt and 12-Bolt Differentials: Depending on the year and model, carrier breaks vary, so consulting specifications is critical.
By referencing manufacturer charts or guides, you can select the correct carrier and gear combination without trial and error.
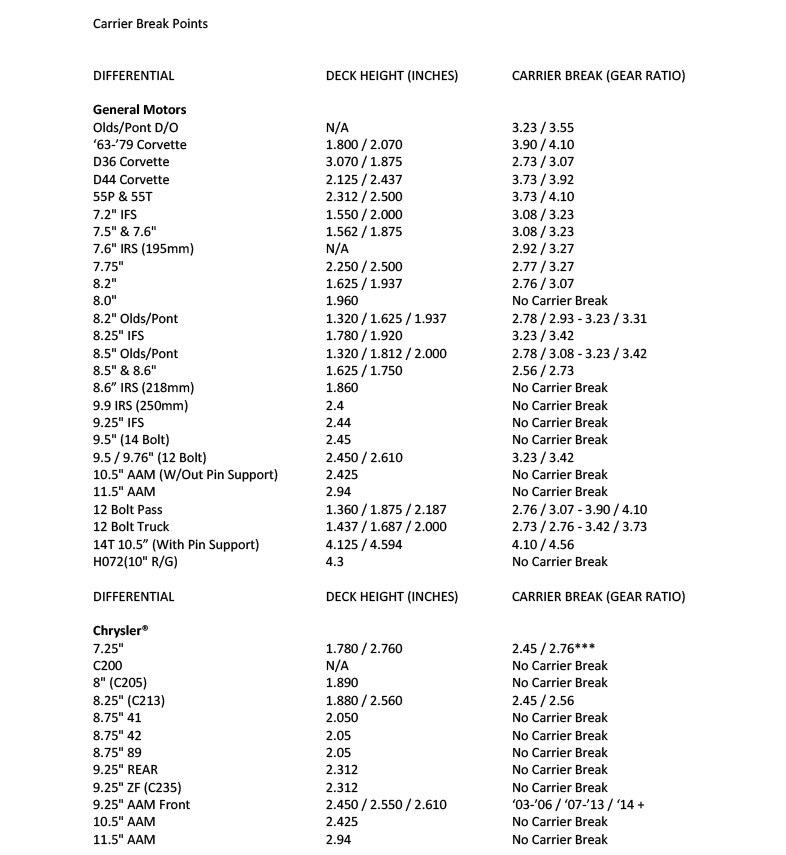
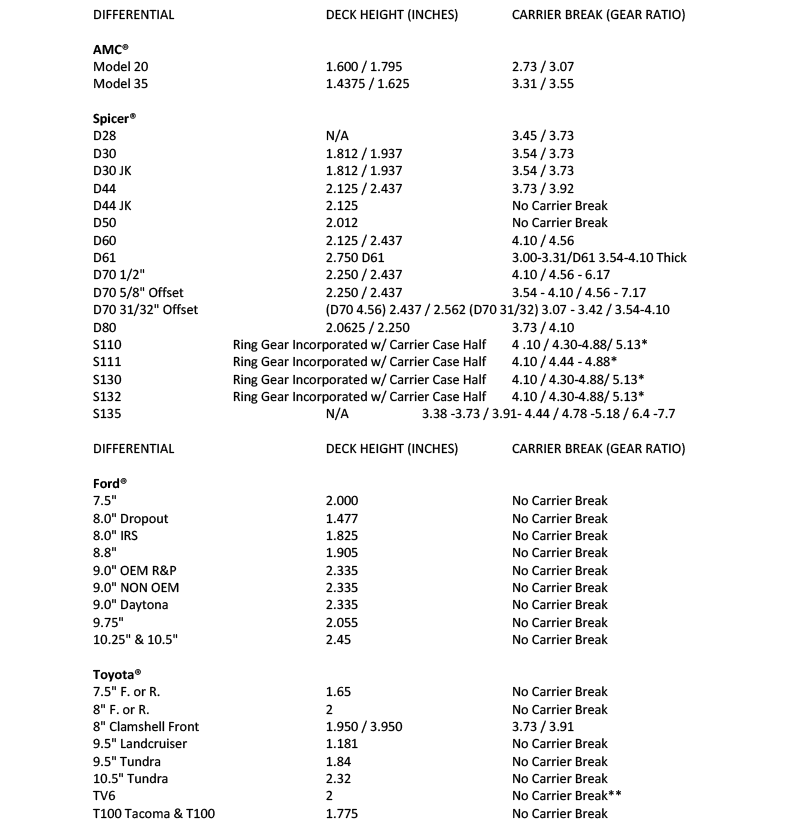
The chart below illustrates the break points and deck height parameters of many of the most popular carriers and differentials. Referencing this chart helps ensure you select the correct carrier and gear combination for your application.
Tips for a Smooth Gear Upgrade
When performing a gear upgrade that involves carrier breaks, consider these tips:
- Use a Professional Installer: Even with the correct gears, precise installation is critical. Proper backlash and gear pattern are essential for quiet, long-lasting operation.
- Consider Bearing Load: Higher torque or larger gears increase stress on differential bearings. Ensure the carrier and bearings are rated for your application.
- Inspect Existing Components: Before upgrading, inspect the current carrier, bearings, and pinion for wear or damage. Reusing worn components can lead to gear failure.
- Upgrade All Related Components: In some cases, upgrading the carrier, ring, pinion, and bearings as a set ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Common Misconceptions About Carrier Breaks
- “Any carrier can handle any ratio.” Incorrect. Carrier break limits are determined by gear thickness and carrier design.
- “A slight modification to the carrier is fine.” Modifying carriers can compromise strength and safety. Only use carriers rated for your gear ratio.
- “Carrier breaks only matter for off-road vehicles.” Incorrect. Even street cars and trucks can experience issues if gear ratios exceed carrier limits.
Conclusion
Understanding carrier breaks is essential for anyone upgrading their differential. Selecting the correct ring and pinion gear, while considering the carrier’s limitations, ensures proper fitment, reliable performance, and long-lasting differential operation.
For enthusiasts looking to upgrade their gear ratios, referencing manufacturer charts, consulting professionals, and considering the full drivetrain setup can prevent costly mistakes. Whether you are upgrading for better off-road traction, improved towing performance, or enhanced acceleration, paying attention to carrier breaks ensures your investment in new gears performs as expected.