Types of Ring Gear Runout
Ring gear runout is primarily categorized into two types:
Radial Runout: This occurs when the ring gear deviates outward or inward relative to its central axis during rotation. Radial runout can cause uneven gear meshing, leading to vibration and noise. In severe cases, it results in excessive localized gear tooth load, overheating, and abnormal wear.
Axial Runout: This refers to the oscillation of the ring gear along the axial direction, causing the gear face to deviate from a uniform plane. Axial runout affects the gear contact pattern, leading to irregular contact pressure distribution. This can reduce meshing rigidity and, in extreme cases, cause gear tooth breakage.
Causes of Ring Gear Runout
The primary causes of ring gear runout include:
- Manufacturing Tolerances:
- Errors during machining, heat treatment, or grinding can lead to surface irregularities.
- Deformation due to heat treatment may affect the geometric accuracy of the ring gear.
- Insufficient precision when mounting the ring gear onto the carrier or flange can exacerbate runout.
- Improper Installation:
- Misalignment during installation or uneven bolt torque can increase runout.
- Insufficient machining precision of the bearing housing or casing may cause unstable meshing between the ring gear and pinion.
- Wear and Deformation:
- Over time, material fatigue can lead to localized ring gear deformation.
- Bearing wear can alter the rotational center of the ring gear, increasing runout.
- Prolonged high-load operation may accelerate uneven wear and loss of roundness.
- Differential Housing or Bearing Seat Issues:
- Inadequate machining precision of the differential housing or main bearing seats can cause excessive runout.
- Incorrect bearing preload can indirectly contribute to abnormal ring gear runout.
Effects of Ring Gear Runout on Vehicle Performance
Excessive ring gear runout can lead to several issues:
- Increased Noise and Vibration:
- Uneven meshing due to runout generates periodic impacts, producing abnormal noise.
- Drivers may experience drivetrain vibrations, especially during acceleration or deceleration.
- Excessive Gear Wear:
- Increased localized contact pressure accelerates gear surface overheating and wear.
- Prolonged uneven meshing can cause gear pitting or flaking.
- Reduced Power Transmission Efficiency:
- Unstable meshing due to runout affects power transmission efficiency.
- Vehicle acceleration and torque response may be compromised, particularly under high torque loads.
- Potential Differential Failure:
- Excessive runout may lead to improper operation of the final drive gear set.
- Long-term high-load operation can result in ring gear cracking or differential failure.
Measurement and Diagnosis of Ring Gear Runout
Ring gear runout is typically measured using the following precision tools:
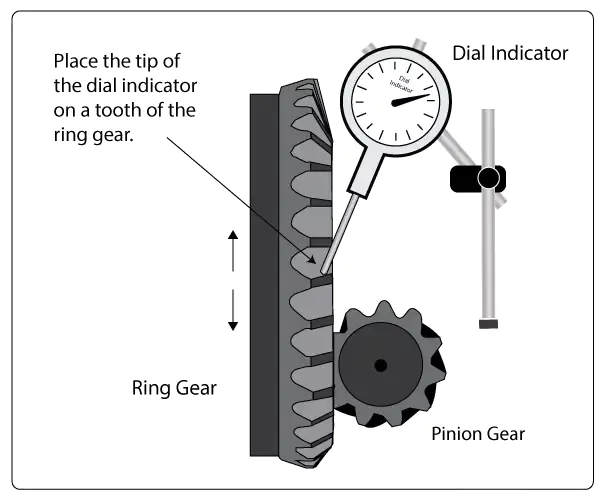
- Dial Indicator:
- Multiple measurement points are selected on the ring gear surface.
- A dial indicator is fixed to measure the maximum and minimum deviations as the ring gear rotates.
- This method is highly accurate and widely used for field inspections.
- Runout Gauge:
- A specialized high-precision instrument designed for measuring runout in laboratory or high-end manufacturing environments.
- Gear Contact Pattern Analysis:
- A contact pattern check is performed by applying marking compound to the gear surface and rotating the gear.
- The contact pattern reveals whether the ring gear is meshing correctly with the pinion.
Permissible Tolerances for Ring Gear Runout
The acceptable runout tolerance varies by application and manufacturer specifications. Generally:
- Automotive ring gears typically have a runout tolerance between 0.002″ to 0.005″ (0.05mm to 0.13mm).
- High-precision industrial gears may have stricter tolerances, often within 0.001″ (0.025mm).
Correction and Prevention of Ring Gear Runout Issues
To minimize ring gear runout, the following measures should be taken:
- Precision Machining:
- Utilize high-precision machine tools during manufacturing to improve accuracy.
- Apply post-heat-treatment correction processes to reduce deformation.
- Ensure flange mounting surfaces are flat to prevent unnecessary assembly stress.
- Proper Installation:
- Use alignment tools during assembly to ensure correct positioning of the ring gear.
- Apply manufacturer-specified torque values evenly when tightening bolts to prevent deformation.
- Component Inspection:
- Regularly inspect the fit accuracy of the differential housing and main bearing seats.
- Monitor bearing wear to prevent excessive play that may cause ring gear misalignment.
- Shimming Adjustments:
- Use shims of appropriate thickness during assembly to achieve optimal positioning.
- During maintenance, fine-tune shim thickness to minimize runout.